
Pes Planus & Pes Cavus (Flat Feet & High Arched Feet)

Pes Planus (flat feet) in children’s podiatry
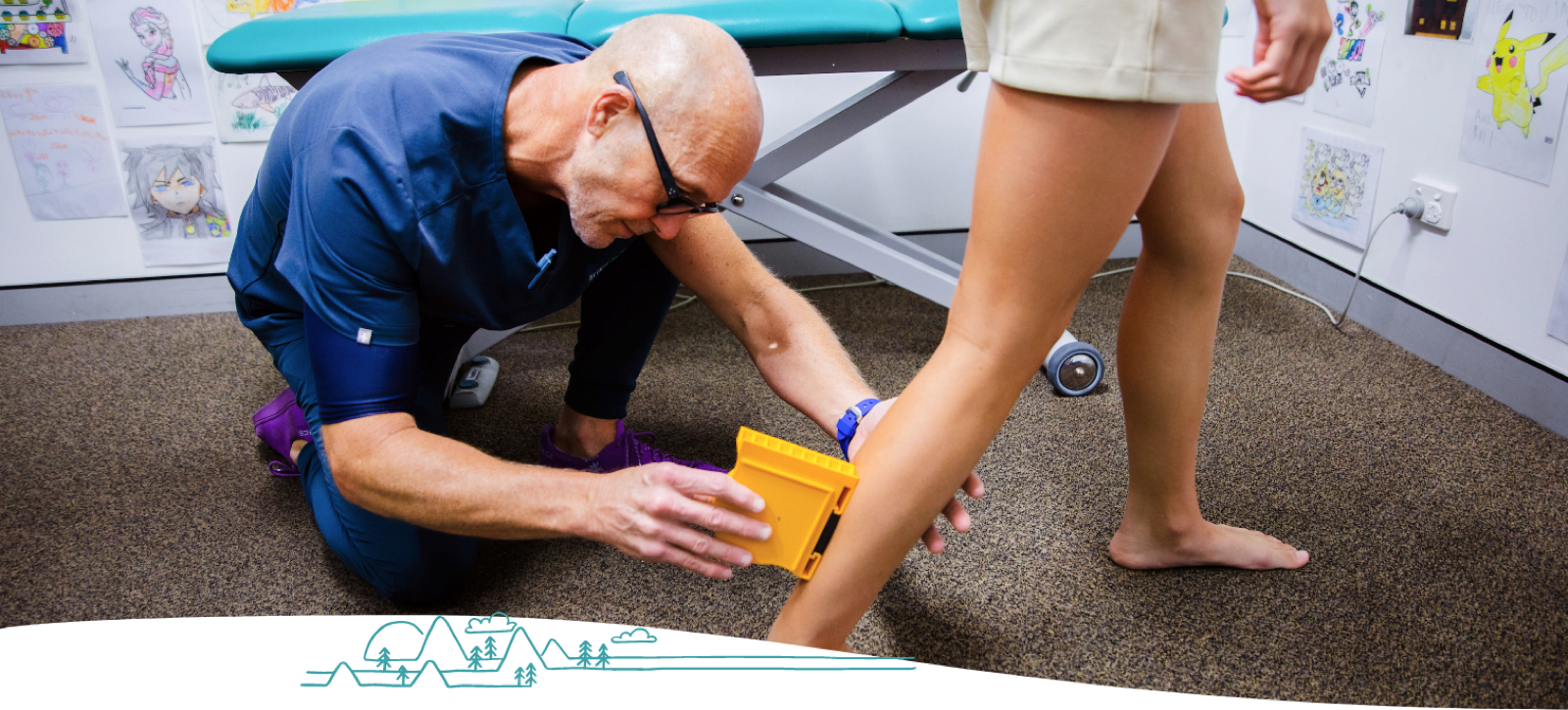
Pes planus, commonly termed flat feet, is one of the most common parental concerns for a child presenting to Little Big Feet, especially when they notice a hereditary likeness to their own feet. Many health professionals also refer to LBF for an assessment of a planus or cavus foot.
First and foremost a child or adolescent must be assessed to determine both the cause and the severity of the presentation.
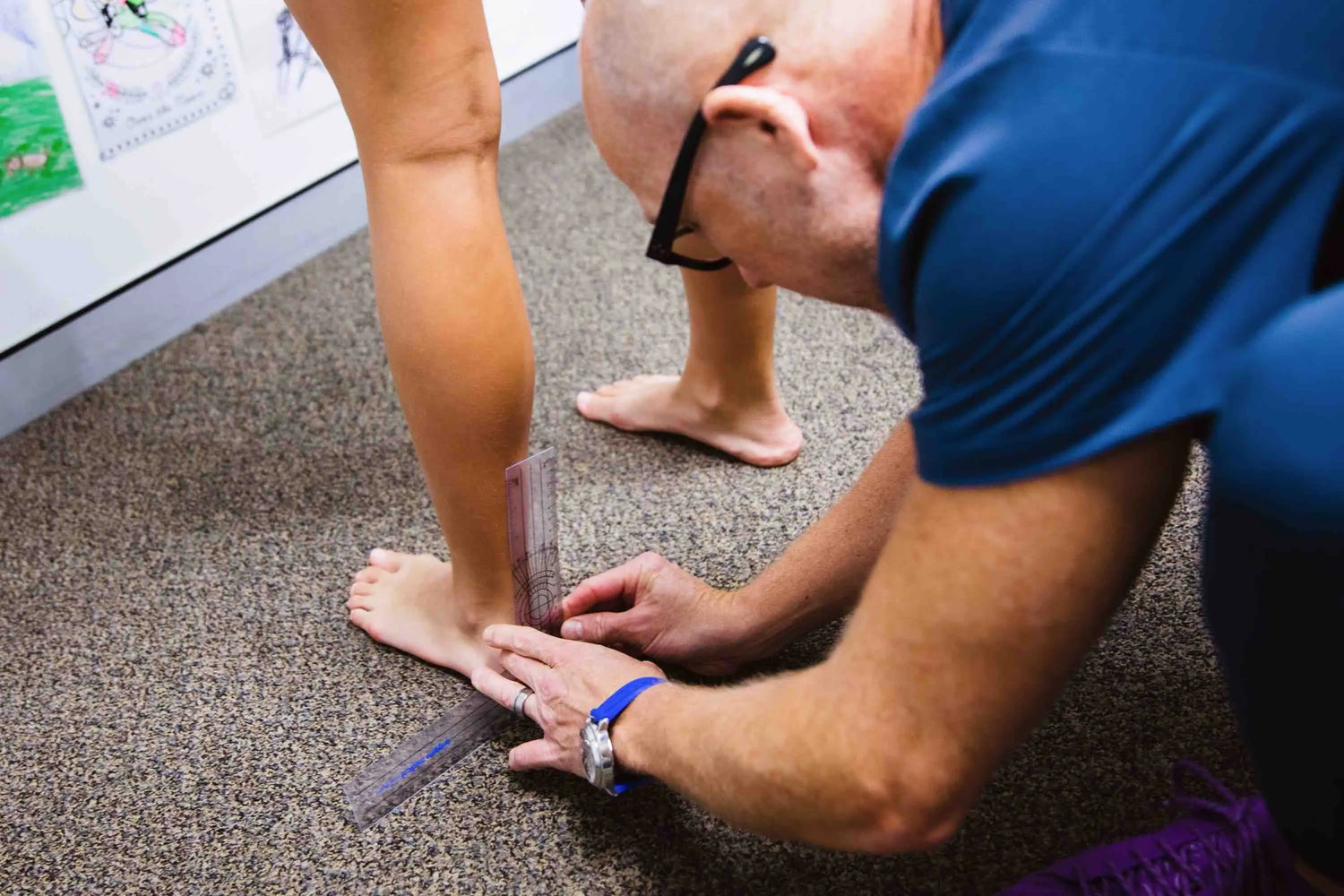
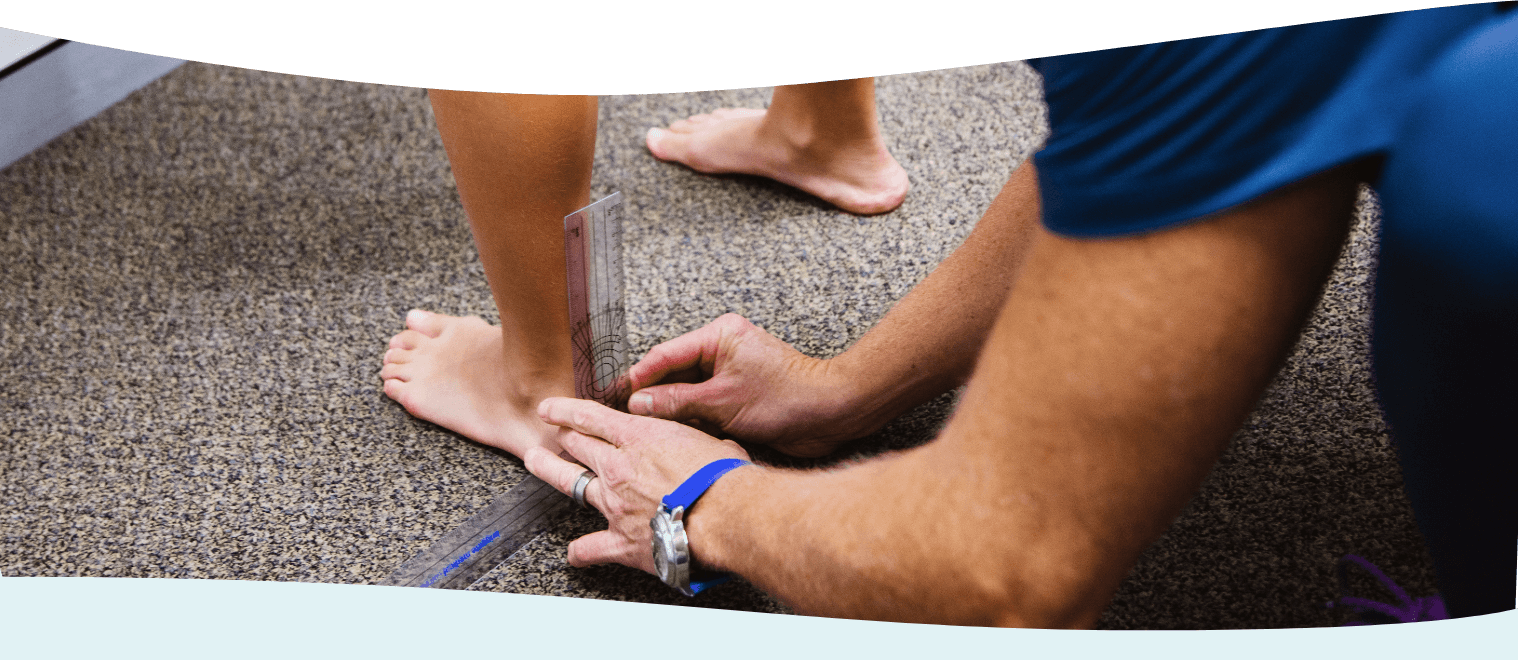
There are many factors which define a planus foot, and the LBF Podiatrists utilise evidence based normative measures to classify a child’s foot based on a Foot Posture Index. Along with a functional assessment and medical history, Podiatrists can determine the severity of the presentation and discuss findings comparatively with what is excusable or acceptable for a child given their age and stage.
In many instances a child’s foot posture is acceptable and considered ‘within normal parameters’ for their age and development. Your Podiatrist will be able explain these findings with you, to determine if and when treatment is warranted.
Treatment of flat foot is dictated by several factors including symptomology, whether the flat foot is complicated or uncomplicated, and the dynamic impact of the presentation (in other words how it affects the child’s function or movement). The reducibility of the flat foot will also affect the treatment selection and outcome.
Pes Cavus (high arch feet) in children’s podiatry
A cavus or high arched foot, is less common than the planus (flat) foot type. Typically, parents or carers will notice other symptomology associated with a cavus foot which may prompt their initial enquiry into a foot assessment. Some of the more common presentations associated with cavus feet include recurrent ankle sprains, and atypical gait or waling pattern, difficulty with footwear selection and restriction in movement of pedal joints.
Whilst it is less common to see, cavus feet may be associated with some congenital anomalies and neurological conditions.
Depending on the findings of a podiatric assessment, treatments for both planus and cavus feet range from simple in-shoe wedging, orthotics and strengthening programs to orthopaedic referral.


Disorders commonly associated with Pes Planus / Pes Cavus
Disorders commonly associated with flat feet in children
- Flexible and/or developmental pes planus foot type
- Hereditary Pes planus
- Acquired Pes Planus
- Congenital Vertical talus (CVT)
- Tarsal Coalition
- Connective tissue diseases
Disorders commonly associated with high arched feet in children
- Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease (CMT)
- Cerebral Palsy (CP)
- Spina Bifida
- Myelomeningocele
- General Neurological Deficiency/Impairment
- Muscle weakness or atrophy








